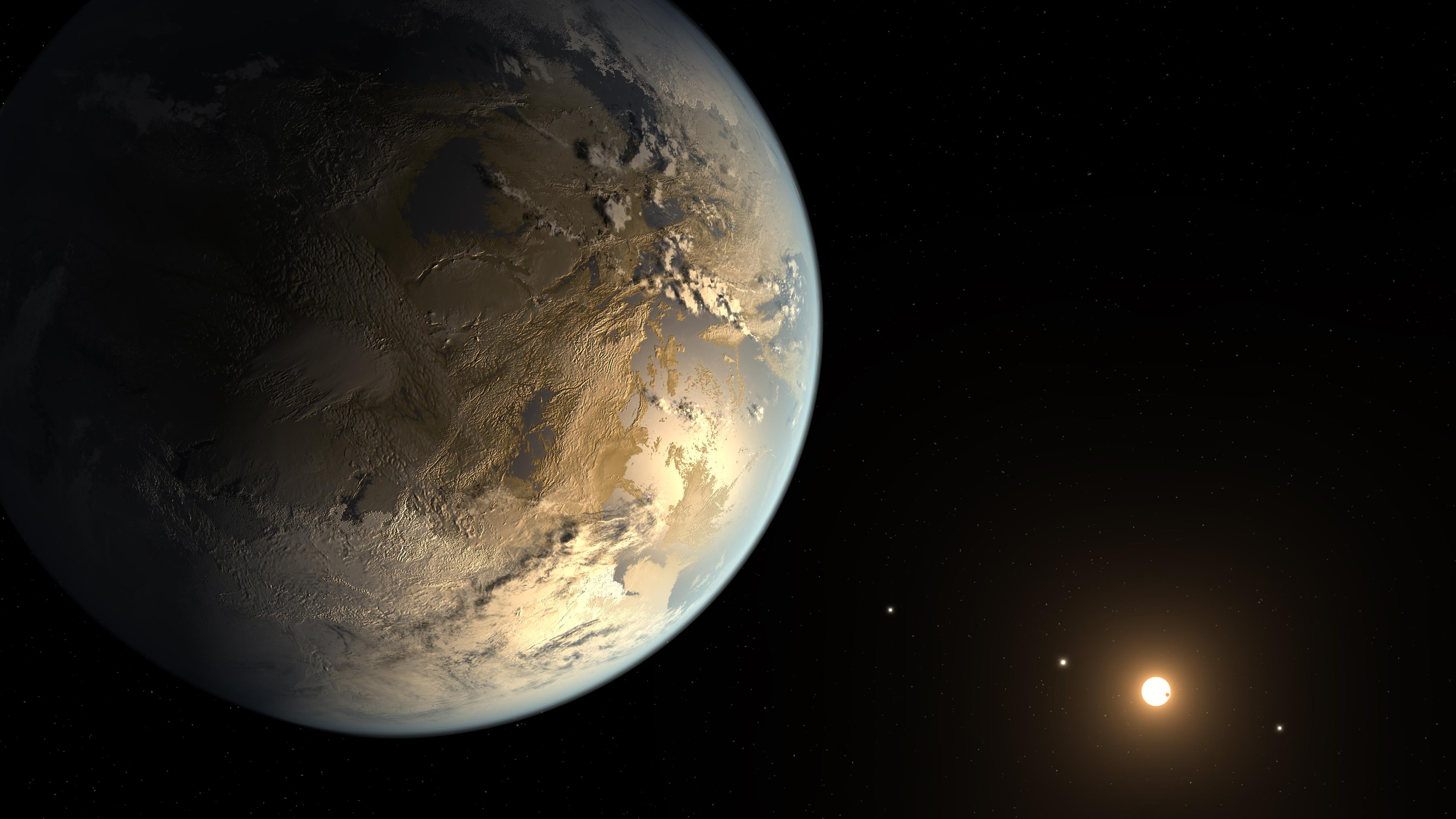
In 2014, NASA discovered an Earth-like planet in the “nearby” solar system, Kepler.
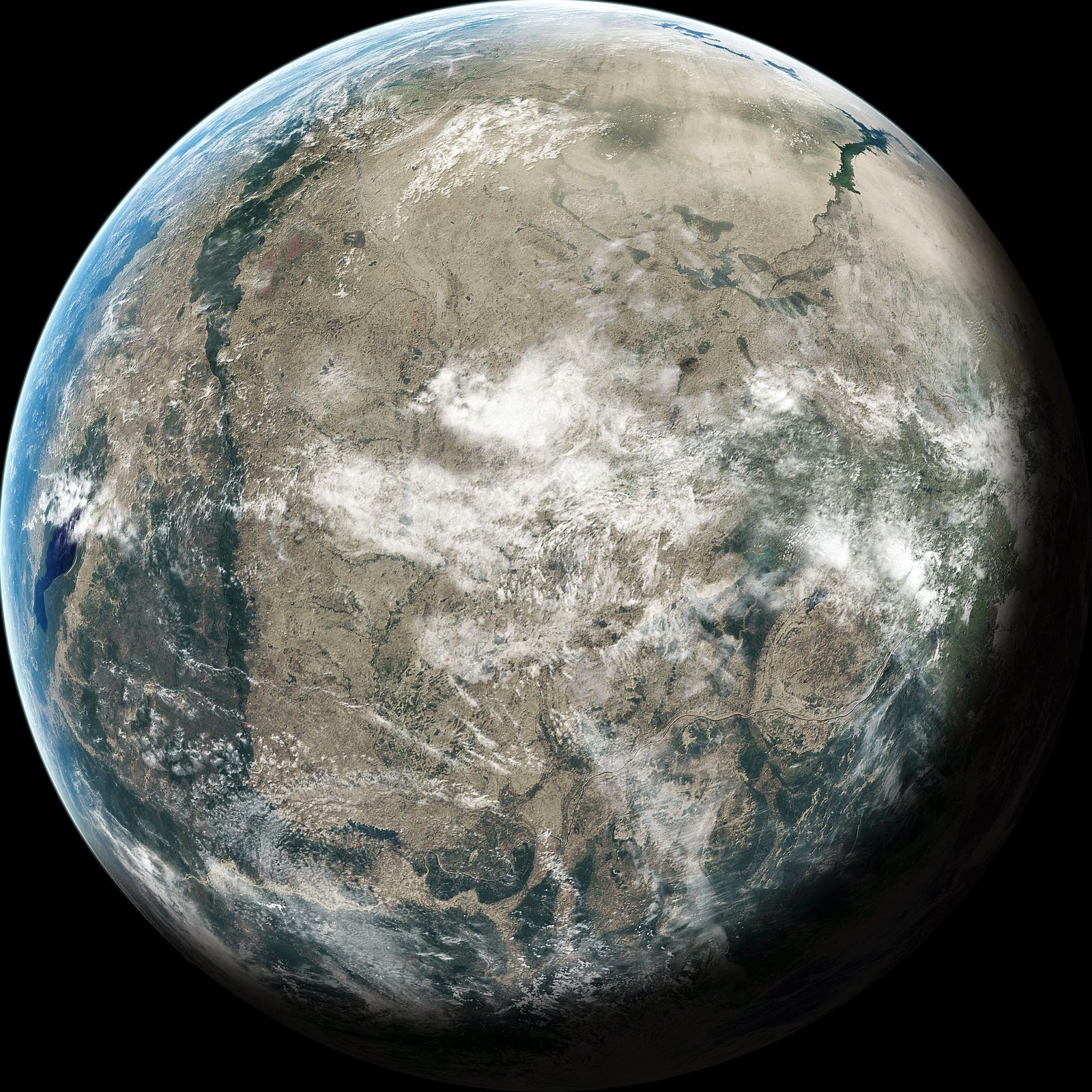
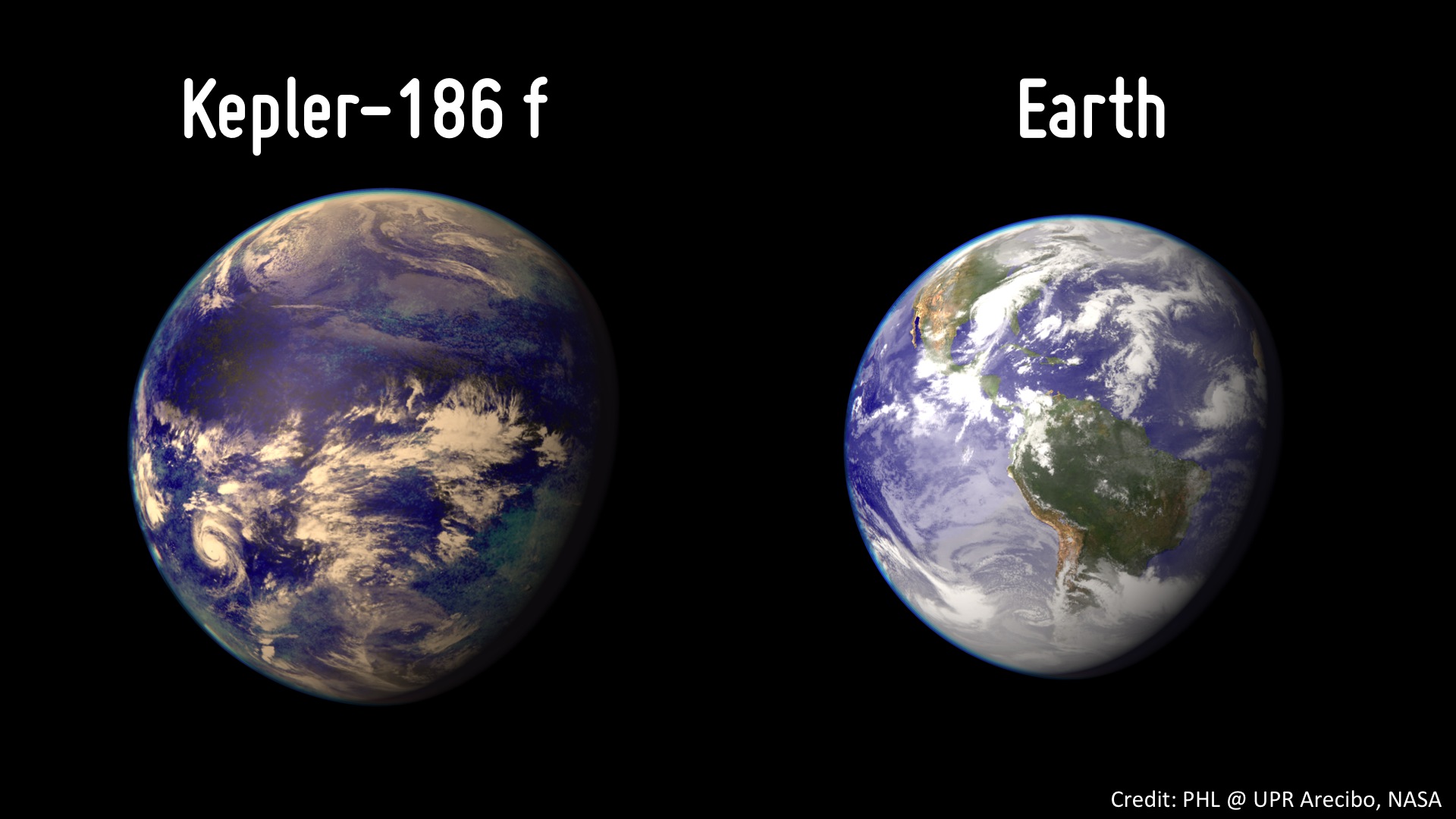
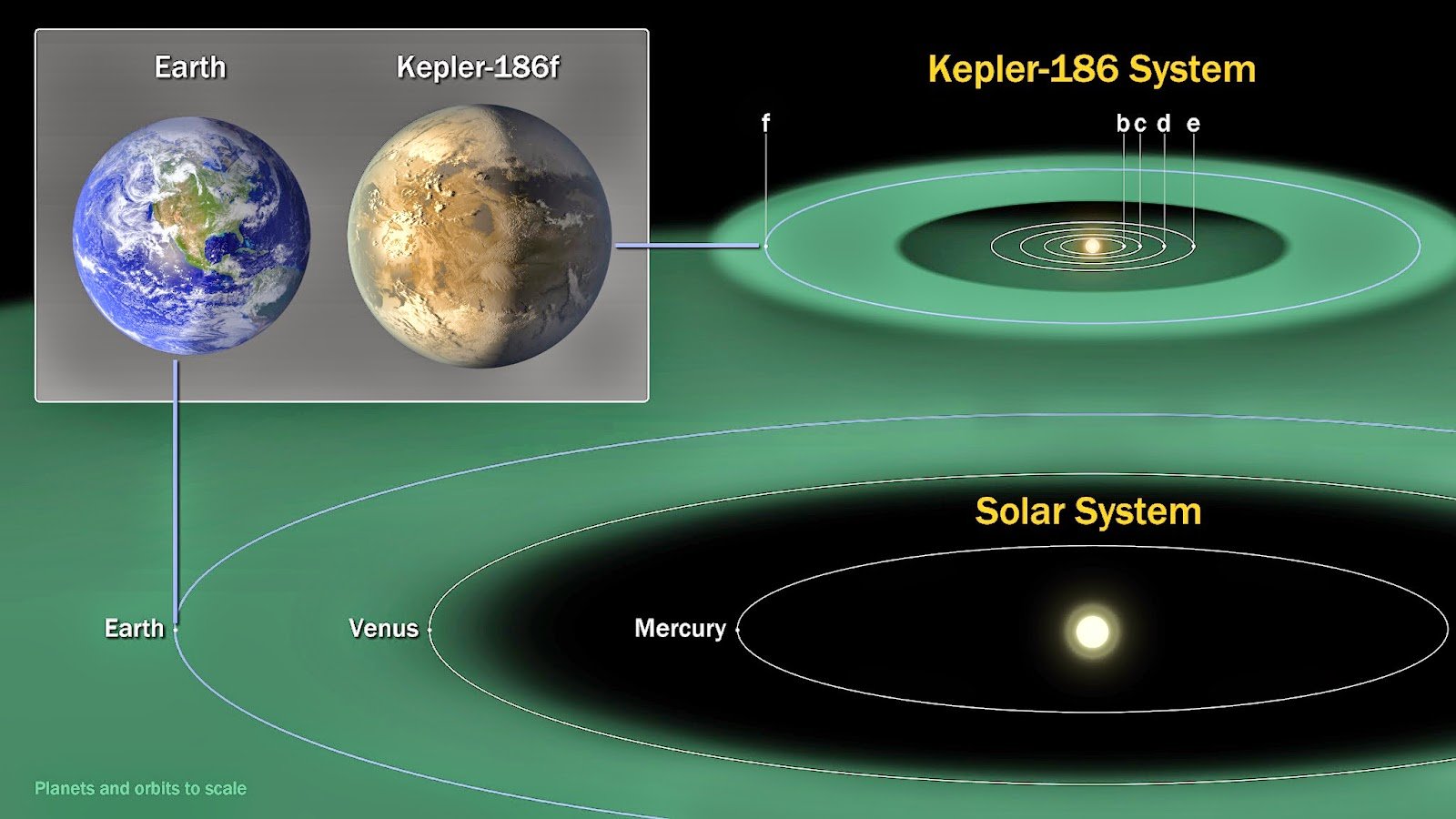
Kepler-186f, the so called Earth’s cousin, is approximately 490 light-years from Earth in the Cygnus constellation.
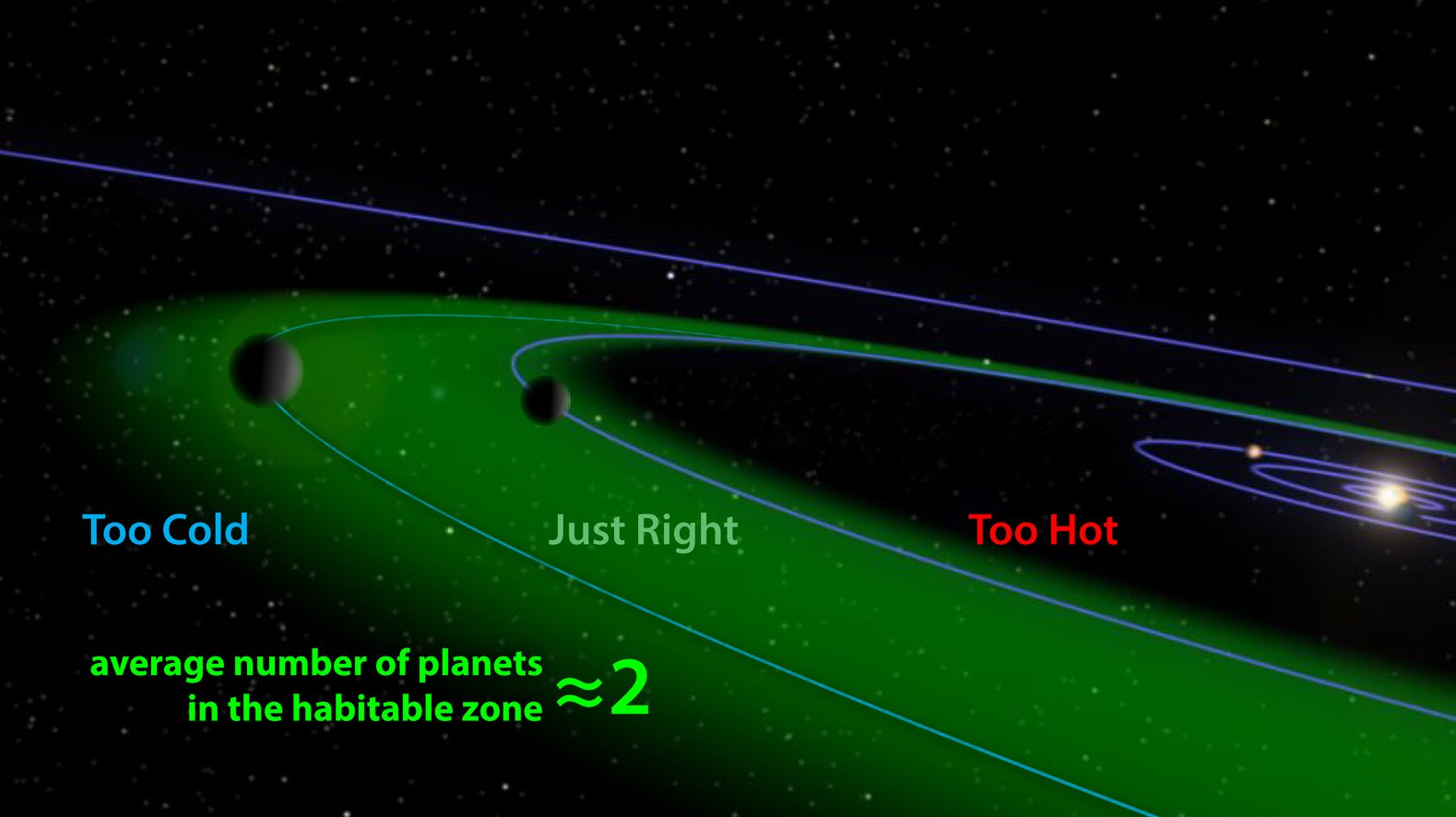
The planet is within the circumstellar habitable zone, also known as the Goldilocks zone, meaning the region around a star (sun) within which planetary-mass objects with sufficient atmospheric pressure can support liquid water at their surfaces.
According to NASA, while planets have previously been found in the habitable zone, they are all at least 40% larger in size than Earth and understanding their makeup is challenging. Kepler-186F is more reminiscent of Earth.
Kepler-186F is closer to its sun in relation to Earth, making its year about 130 days long.
Its average surface temperature, however, is considered to be close to earth’s, due to the lower luminosity of its star.
Astronomers believe that its orbit is high enough to escape gravitational locking (tidal locking), thus allowing it to self-rotate, although in a much slower way than Earth does. This means that its days and nights probably last for weeks or maybe even months.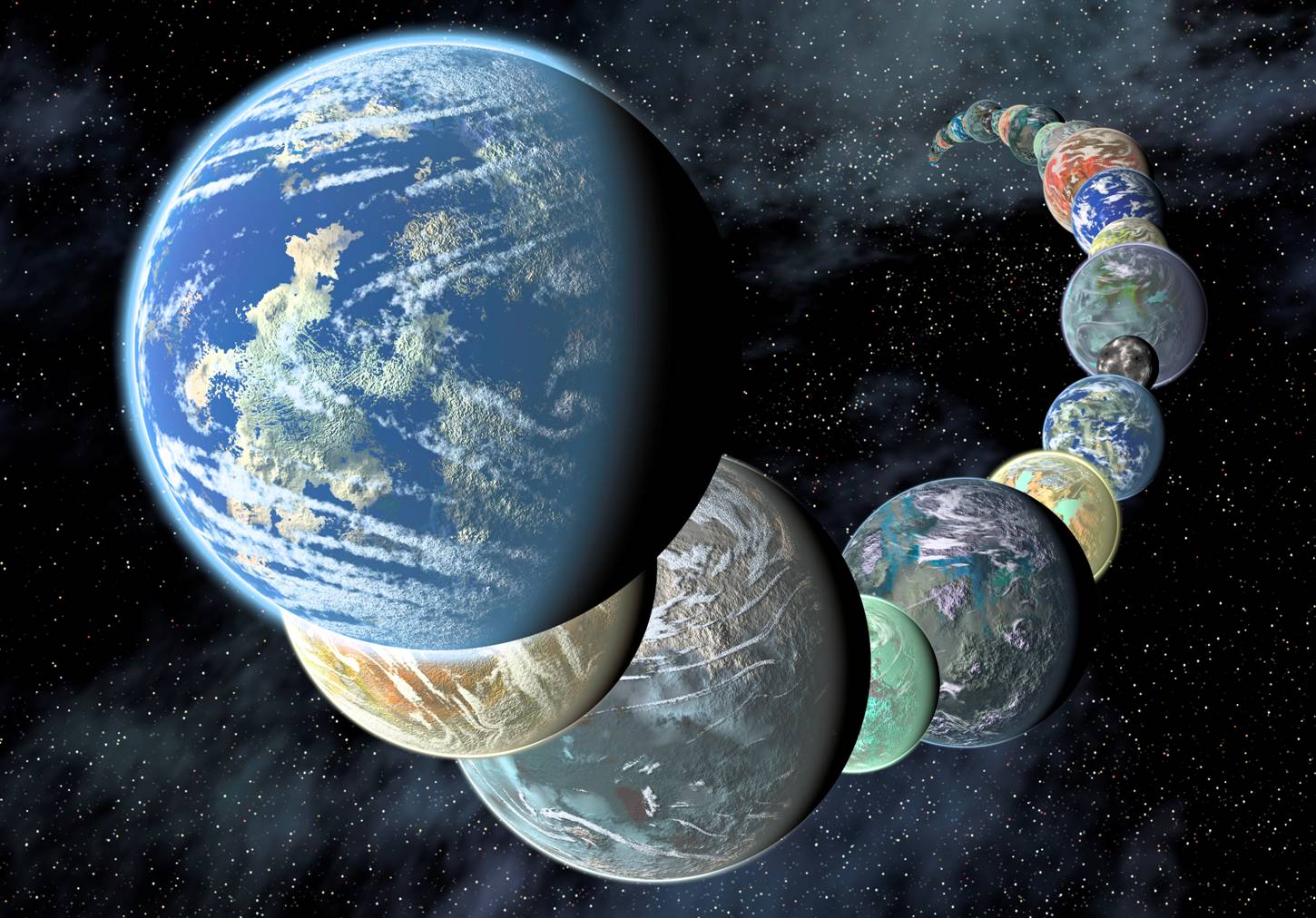
NASA Illustration of the Planets discovered by the Kepler telescope
“We know of just one planet where life exists — Earth. When we search for life outside our solar system we focus on finding planets with characteristics that mimic that of Earth. Finding a habitable zone planet comparable to Earth in size is a major step forward”, said Elisa Quintana, research scientist at the SETI Institute at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California.