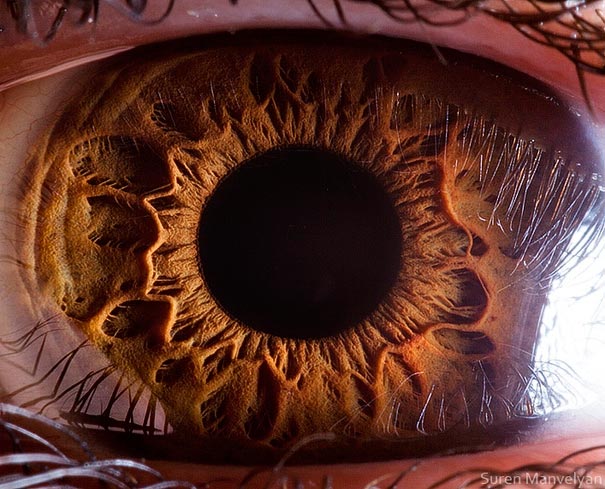
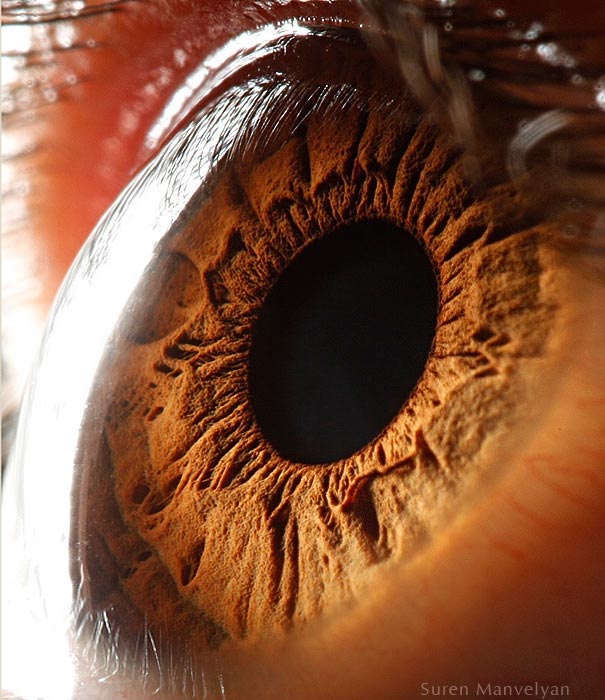
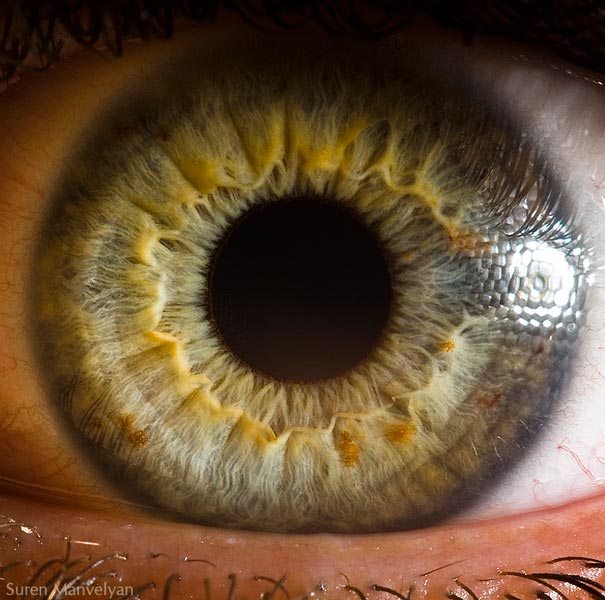
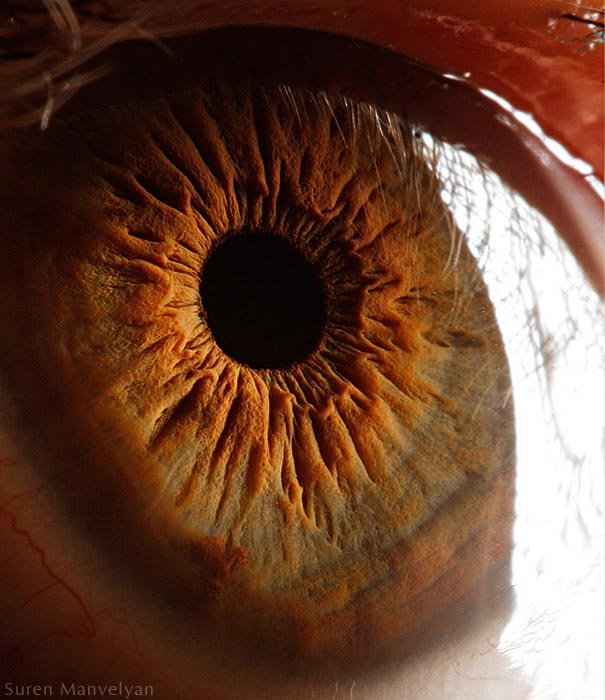
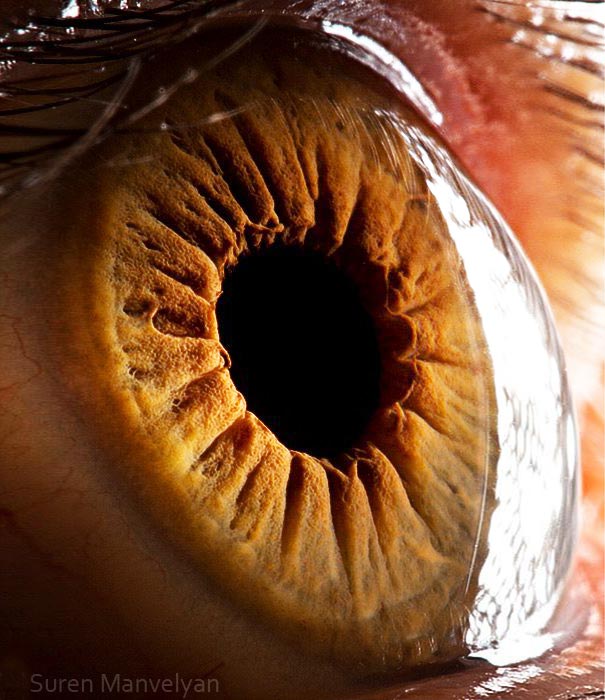
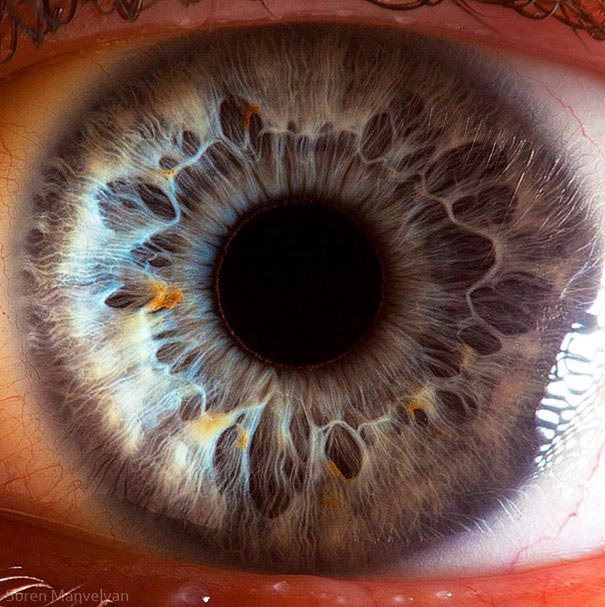
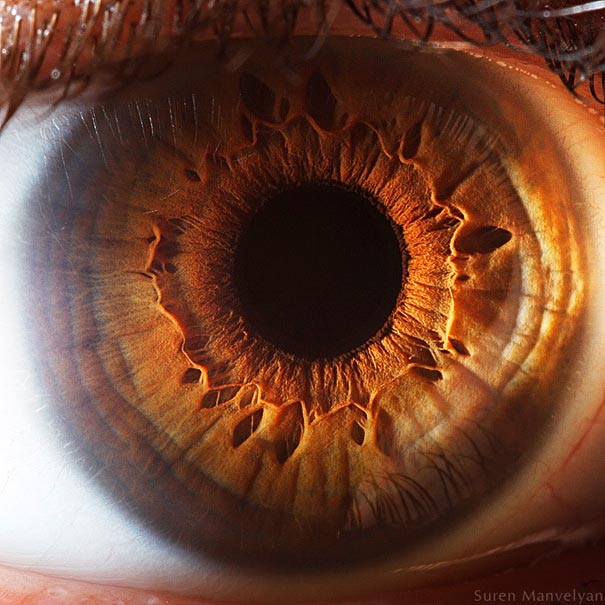
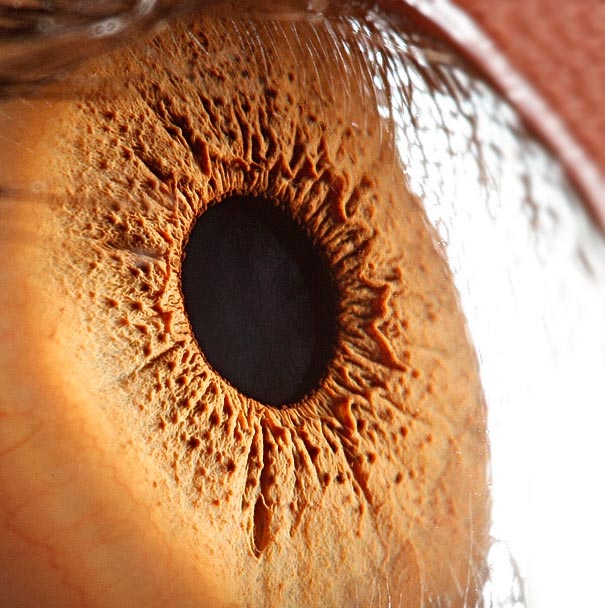
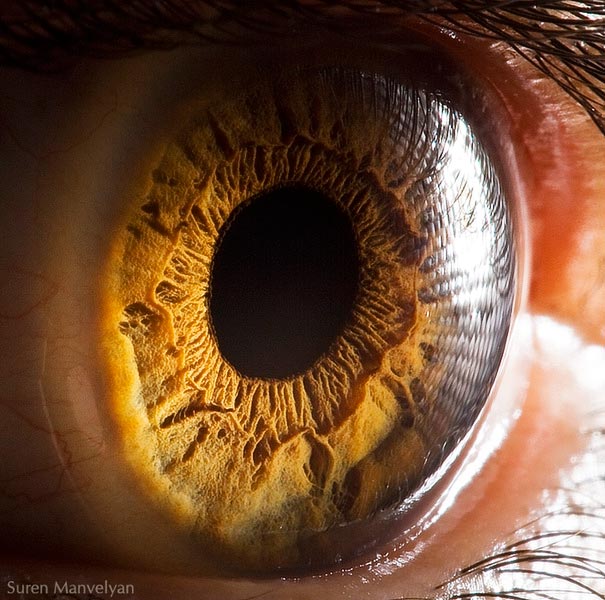
The average human retina has five million cone receptors on it. Since the cones are responsible for colour vision, you might suppose that this equates to a five megapixel equivilant for the human eye.
But there are also a hundred million rods that detect monochrome contrast, which plays an important role in the sharpness of the image you see. And even this 105MP is an underestimate because the eye is not a still camera.
You have two eyes (no kidding!) and they continually flick around to cover a much larger area than your field of view and the composite image is assembled in the brain – not unlike stitching together a panoramic photo. In good light, you can distinguish two fine lines if they are seperate by at least 0.6 arc-minutes (0.01.Degrees).
This gives an equivilant pixel size of 0.3 arc-minutes. If you take a conservative 120 degrees as your horizontal field of view and 60 degrees in the vertical plane, this translates to …
576 megapixels of available image data.
Curiously – as a counterpoint to this – most people cannot distinguish the difference in quality between a 300dpi and a 150dpi photo when printed at 6×4″, when viewed at normal viewing distances.
So: although the human eye and brain when combined can resolve massive amounts of data, for imaging purposes, 150dpi output is more than enough to provide adequate data for us to accept the result as photographic quality.
But don’t forget that women have more cones and men have more rods – I kid you not.Therefore the ladies see colours brighter than gents but can’t see as well when it gets dark.
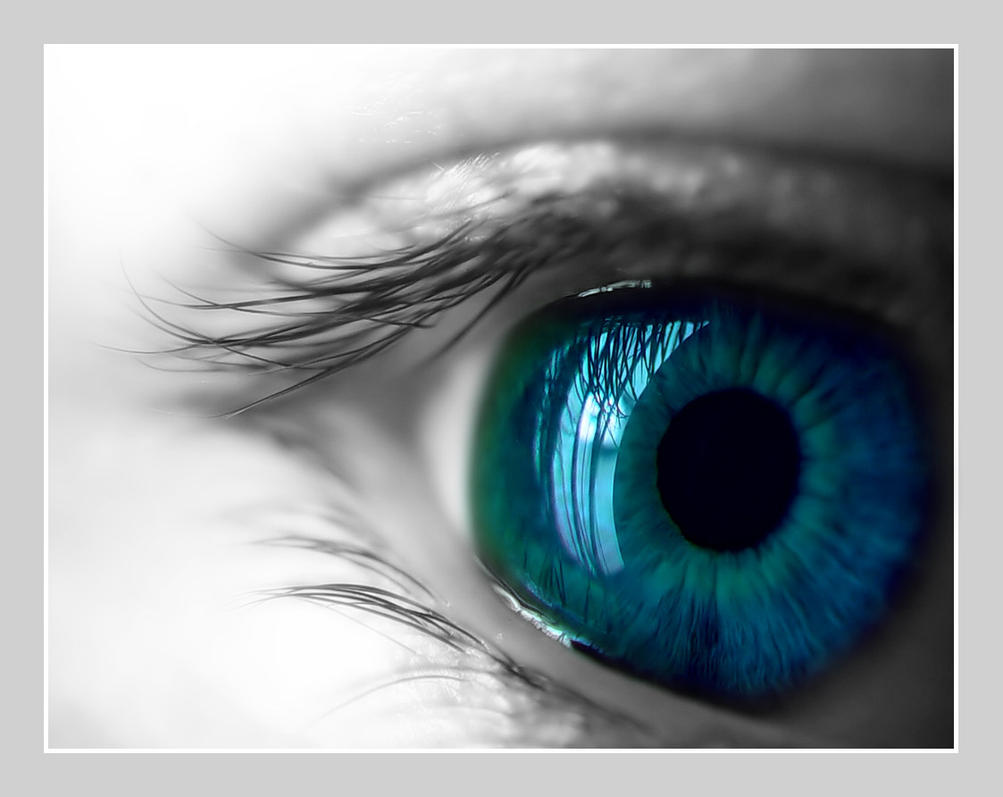

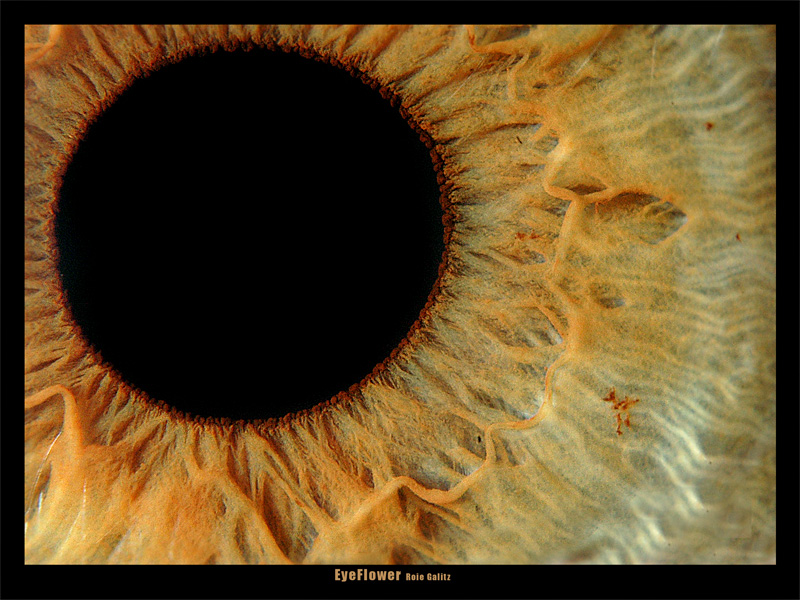
The new iPhone camera is 8-megapixels. Meanwhile, Canon is reportedly testing a new DSLR with 75-megapixels. But how many megapixels is the human eye? That is, how many megapixels would an image the size of your field of vision need to be to look normal?
Well, as Vsauce explains in its latest video, the better question is actually: What is the resolution of the human eye?
It’s a complicated question, one that must take into account the peculiar anatomy of the eye which is different than the less peculiar engineering of a digital camera. As such, it’s worth watching all ten minutes of the video, explaining not only how we see but also how well. Spoiler: the human eye is 576 megapixels—but really only about 7 megapixels matter.